pertpy.tools.Sccoda¶
- class pertpy.tools.Sccoda(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Statistical model for single-cell differential composition analysis with specification of a reference cell type. This is the standard scCODA model and recommended for all uses.
The hierarchical formulation of the model for one sample is:
\[\begin{split}y|x &\sim DirMult(\phi, \bar{y}) \\ \log(\phi) &= \alpha + x \beta \\ \alpha_k &\sim N(0, 5) \quad &\forall k \in [K] \\ \beta_{m, \hat{k}} &= 0 &\forall m \in [M]\\ \beta_{m, k} &= \tau_{m, k} \tilde{\beta}_{m, k} \quad &\forall m \in [M], k \in \{[K] \smallsetminus \hat{k}\} \\ \tau_{m, k} &= \frac{\exp(t_{m, k})}{1+ \exp(t_{m, k})} \quad &\forall m \in [M], k \in \{[K] \smallsetminus \hat{k}\} \\ \frac{t_{m, k}}{50} &\sim N(0, 1) \quad &\forall m \in [M], k \in \{[K] \smallsetminus \hat{k}\} \\ \tilde{\beta}_{m, k} &= \sigma_m^2 \cdot \gamma_{m, k} \quad &\forall m \in [M], k \in \{[K] \smallsetminus \hat{k}\} \\ \sigma_m^2 &\sim HC(0, 1) \quad &\forall m \in [M] \\ \gamma_{m, k} &\sim N(0,1) \quad &\forall m \in [M], k \in \{[K] \smallsetminus \hat{k}\} \\\end{split}\]with y being the cell counts and x the covariates.
For further information, see scCODA is a Bayesian model for compositional single-cell data analysis (Büttner, Ostner et al., NatComms, 2021)
Methods table¶
|
Decides which effects of the scCODA model are credible based on an adjustable inclusion probability threshold. |
|
Get effect dataframe as printed in the extended summary |
|
Get intercept dataframe as printed in the extended summary |
|
Get node effect dataframe as printed in the extended summary of a tascCODA model |
|
Prepare a MuData object for subsequent processing. |
|
Creates arviz object from model results for MCMC diagnosis |
|
Implements scCODA model in numpyro |
|
Handles data preprocessing, covariate matrix creation, reference selection, and zero count replacement for scCODA. |
|
Run standard Hamiltonian Monte Carlo sampling (Neal, 2011) to infer optimal model parameters. |
|
Run No-U-turn sampling (Hoffman and Gelman, 2014), an efficient version of Hamiltonian Monte Carlo sampling to infer optimal model parameters. |
|
Direct posterior probability approach to calculate credible effects while keeping the expected FDR at a certain level |
|
Sets initial MCMC state values for scCODA model |
|
Printing method for the summary. |
|
Generates summary dataframes for intercepts, effects and node-level effect (if using tree aggregation). |
|
Grouped boxplot visualization. |
|
Plot a tree with colored circles on the nodes indicating significant effects with bar plots which indicate leave-level significant effects. |
|
Plot a tree using input ete3 tree object. |
|
Barplot visualization for effects. |
|
Plot a UMAP visualization colored by effect strength. |
|
Plots total variance of relative abundance versus minimum relative abundance of all cell types for determination of a reference cell type. |
|
Plots a stacked barplot for all levels of a covariate or all samples (if feature_name=="samples"). |
Methods¶
credible_effects¶
- Sccoda.credible_effects(data, modality_key='coda', est_fdr=None)[source]¶
- Decides which effects of the scCODA model are credible based on an adjustable inclusion probability threshold.
Note: Parameter est_fdr has no effect for spike-and-slab LASSO selection method
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Credible effect decision series which includes boolean values indicate whether effects are credible under inc_prob_threshold.
- Return type:
pd.Series
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> credible_effects = sccoda.credible_effects(mdata)
get_effect_df¶
- Sccoda.get_effect_df(data, modality_key='coda')¶
Get effect dataframe as printed in the extended summary
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Effect data frame.
- Return type:
pd.DataFrame
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> effects = sccoda.get_effect_df(mdata)
get_intercept_df¶
- Sccoda.get_intercept_df(data, modality_key='coda')¶
Get intercept dataframe as printed in the extended summary
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Intercept data frame.
- Return type:
pd.DataFrame
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> intercepts = sccoda.get_intercept_df(mdata)
get_node_df¶
- Sccoda.get_node_df(data, modality_key='coda')¶
Get node effect dataframe as printed in the extended summary of a tascCODA model
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Node effect data frame.
- Return type:
pd.DataFrame
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> adata = pt.dt.tasccoda_example() >>> tasccoda = pt.tl.Tasccoda() >>> mdata = tasccoda.load( >>> adata, type="sample_level", >>> levels_agg=["Major_l1", "Major_l2", "Major_l3", "Major_l4", "Cluster"], >>> key_added="lineage", add_level_name=True >>> ) >>> mdata = tasccoda.prepare( >>> mdata, formula="Health", reference_cell_type="automatic", tree_key="lineage", pen_args={"phi": 0} >>> ) >>> tasccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_samples=1000, num_warmup=100, rng_key=42) >>> node_effects = tasccoda.get_node_df(mdata)
load¶
- Sccoda.load(adata, type, generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier=None, sample_identifier=None, covariate_uns=None, covariate_obs=None, covariate_df=None, modality_key_1='rna', modality_key_2='coda')[source]¶
Prepare a MuData object for subsequent processing. If type is “cell_level”, then create a compositional analysis dataset from the input adata.
When using
type="cell_level",adataneeds to have a column inadata.obsthat contains the cell type assignment. Further, it must contain one column or a set of columns (e.g. subject id, treatment, disease status) that uniquely identify each (statistical) sample. Further covariates (e.g. subject age) can either be specified via addidional column names inadata.obs, a key inadata.uns, or as a separate DataFrame.- Parameters:
adata (
AnnData) – AnnData object.type (
Literal['cell_level','sample_level']) – Specify the input adata type, which could be either a cell-level AnnData or an aggregated sample-level AnnData.generate_sample_level (
bool) – Whether to generate an AnnData object on the sample level or create an empty AnnData object.cell_type_identifier (
str) – If type is “cell_level”, specify column name in adata.obs that specifies the cell types. Defaults to None.sample_identifier (
str) – If type is “cell_level”, specify column name in adata.obs that specifies the sample. Defaults to None.covariate_uns (
str|None) – If type is “cell_level”, specify key for adata.uns, where covariate values are stored. Defaults to None.covariate_obs (
list[str] |None) – If type is “cell_level”, specify list of keys for adata.obs, where covariate values are stored. Defaults to None.covariate_df (
DataFrame|None) – If type is “cell_level”, specify dataFrame with covariates. Defaults to None.modality_key_1 (
str) – Key to the cell-level AnnData in the MuData object. Defaults to “rna”.modality_key_2 (
str) – Key to the aggregated sample-level AnnData object in the MuData object. Defaults to “coda”.
- Returns:
MuData object with cell-level AnnData (mudata[modality_key_1]) and aggregated sample-level AnnData (mudata[modality_key_2]).
- Return type:
MuData
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"])
make_arviz¶
- Sccoda.make_arviz(data, modality_key='coda', rng_key=None, num_prior_samples=500, use_posterior_predictive=True)[source]¶
Creates arviz object from model results for MCMC diagnosis
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.rng_key – The rng state used for the prior simulation. If None, a random state will be selected. Defaults to None.
num_prior_samples (
int) – Number of prior samples calculated. Defaults to 500.use_posterior_predictive (
bool) – If True, the posterior predictive will be calculated. Defaults to True.
- Returns:
arviz_data with all MCMC information
- Return type:
az.InferenceData
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> arviz_data = sccoda.make_arviz(mdata, num_prior_samples=100)
model¶
plot_boxplots¶
- Sccoda.plot_boxplots(data, feature_name, modality_key='coda', y_scale='relative', plot_facets=False, add_dots=False, cell_types=None, args_boxplot=None, args_swarmplot=None, palette='Blues', show_legend=True, level_order=None, figsize=None, dpi=100, return_fig=None, ax=None, show=None, save=None)¶
Grouped boxplot visualization.
The cell counts for each cell type are shown as a group of boxplots with intra–group separation by a covariate from data.obs.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData objectfeature_name (
str) – The name of the feature in data.obs to plotmodality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.y_scale (
Literal['relative','log','log10','count']) – Transformation to of cell counts. Options: “relative” - Relative abundance, “log” - log(count), “log10” - log10(count), “count” - absolute abundance (cell counts). Defaults to “relative”.plot_facets (
bool) – If False, plot cell types on the x-axis. If True, plot as facets. Defaults to False.add_dots (
bool) – If True, overlay a scatterplot with one dot for each data point. Defaults to False.cell_types (
list|None) – Subset of cell types that should be plotted. Defaults to None.args_boxplot (
dict|None) – Arguments passed to sns.boxplot. Defaults to {}.args_swarmplot (
dict|None) – Arguments passed to sns.swarmplot. Defaults to {}.figsize (
tuple[float,float] |None) – Figure size. Defaults to None.palette (
str|None) – The seaborn color map for the barplot. Defaults to “Blues”.show_legend (
bool|None) – If True, adds a legend. Defaults to True.level_order (
list[str]) – Custom ordering of bars on the x-axis. Defaults to None.
- Return type:
- Returns:
Depending on plot_facets, returns a
Axes(plot_facets = False) orFacetGrid(plot_facets = True) object
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> sccoda.plot_boxplots(mdata, feature_name="condition", add_dots=True)
- Preview:
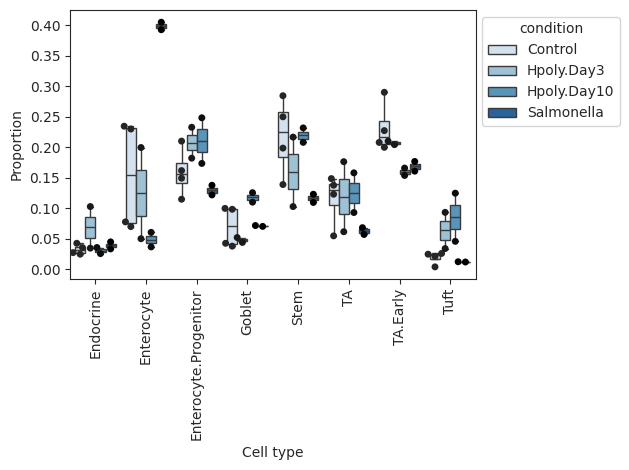
plot_draw_effects¶
- Sccoda.plot_draw_effects(data, covariate, modality_key='coda', tree='tree', show_legend=None, show_leaf_effects=False, tight_text=False, show_scale=False, units='px', figsize=(None, None), dpi=100, show=True, save=None)¶
Plot a tree with colored circles on the nodes indicating significant effects with bar plots which indicate leave-level significant effects.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.covariate (
str) – The covariate, whose effects should be plotted.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.tree (
str) – A ete3 tree object or a str to indicate the tree stored in .uns. Defaults to “tree”.show_legend (
bool|None) – If show legend of nodes significant effects or not. Defaults to False if show_leaf_effects is True.show_leaf_effects (
bool|None) – If True, plot bar plots which indicate leave-level significant effects. Defaults to False.tight_text (
bool|None) – When False, boundaries of the text are approximated according to general font metrics, producing slightly worse aligned text faces but improving the performance of tree visualization in scenes with a lot of text faces. Defaults to False.show_scale (
bool|None) – Include the scale legend in the tree image or not. Defaults to False.show (
bool|None) – If True, plot the tree inline. If false, return tree and tree_style objects. Defaults to True.file_name – Path to the output image file. valid extensions are .SVG, .PDF, .PNG. Output image can be saved whether show is True or not. Defaults to None.
units (
Optional[Literal['px','mm','in']]) – Unit of image sizes. “px”: pixels, “mm”: millimeters, “in”: inches. Defaults to “px”.figsize (
tuple[float,float] |None) – Figure size. Defaults to None.
- Return type:
TreeNode|None- Returns:
Depending on show, returns
ete3.TreeNodeandete3.TreeStyle(show = False) or plot the tree inline (show = False)
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> adata = pt.dt.tasccoda_example() >>> tasccoda = pt.tl.Tasccoda() >>> mdata = tasccoda.load( >>> adata, type="sample_level", >>> levels_agg=["Major_l1", "Major_l2", "Major_l3", "Major_l4", "Cluster"], >>> key_added="lineage", add_level_name=True >>> ) >>> mdata = tasccoda.prepare( >>> mdata, formula="Health", reference_cell_type="automatic", tree_key="lineage", pen_args={"phi": 0} >>> ) >>> tasccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_samples=1000, num_warmup=100, rng_key=42) >>> tasccoda.plot_draw_effects(mdata, covariate="Health[T.Inflamed]", tree="lineage")
- Preview:
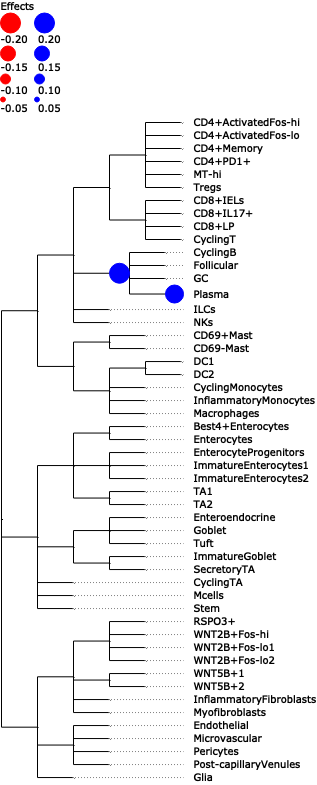
plot_draw_tree¶
- Sccoda.plot_draw_tree(data, modality_key='coda', tree='tree', tight_text=False, show_scale=False, units='px', figsize=(None, None), dpi=100, show=True, save=None)¶
Plot a tree using input ete3 tree object.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.tree (
str) – A ete3 tree object or a str to indicate the tree stored in .uns. Defaults to “tree”.tight_text (
bool|None) – When False, boundaries of the text are approximated according to general font metrics, producing slightly worse aligned text faces but improving the performance of tree visualization in scenes with a lot of text faces. Default to False.show_scale (
bool|None) – Include the scale legend in the tree image or not. Defaults to False.show (
bool|None) – If True, plot the tree inline. If false, return tree and tree_style objects. Defaults to True.file_name – Path to the output image file. Valid extensions are .SVG, .PDF, .PNG. Output image can be saved whether show is True or not. Defaults to None.
units (
Optional[Literal['px','mm','in']]) – Unit of image sizes. “px”: pixels, “mm”: millimeters, “in”: inches. Defaults to “px”.figsize (
tuple[float,float] |None) – Figure size. Defaults to None.
- Return type:
TreeNode|None- Returns:
Depending on show, returns
ete3.TreeNodeandete3.TreeStyle(show = False) or plot the tree inline (show = False)
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> adata = pt.dt.tasccoda_example() >>> tasccoda = pt.tl.Tasccoda() >>> mdata = tasccoda.load( >>> adata, type="sample_level", >>> levels_agg=["Major_l1", "Major_l2", "Major_l3", "Major_l4", "Cluster"], >>> key_added="lineage", add_level_name=True >>> ) >>> mdata = tasccoda.prepare( >>> mdata, formula="Health", reference_cell_type="automatic", tree_key="lineage", pen_args={"phi": 0} >>> ) >>> tasccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_samples=1000, num_warmup=100, rng_key=42) >>> tasccoda.plot_draw_tree(mdata, tree="lineage")
- Preview:
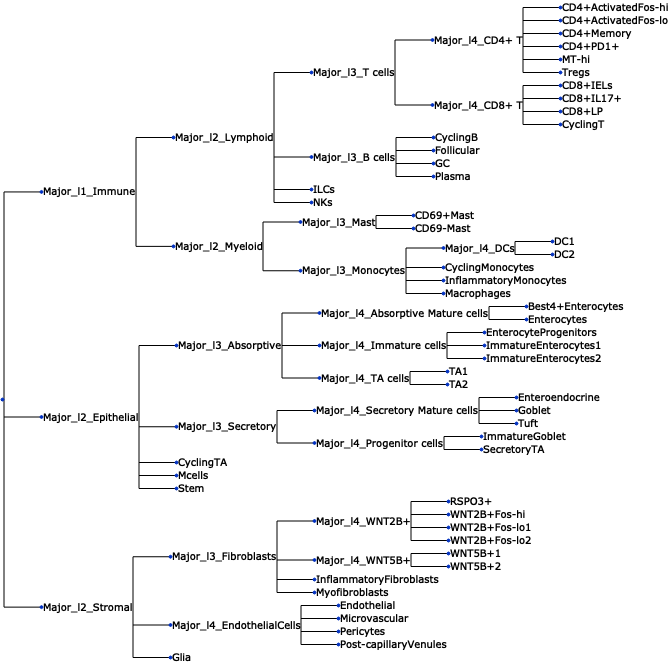
plot_effects_barplot¶
- Sccoda.plot_effects_barplot(data, modality_key='coda', covariates=None, parameter='log2-fold change', plot_facets=True, plot_zero_covariate=True, plot_zero_cell_type=False, palette=<matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap object>, level_order=None, args_barplot=None, figsize=None, dpi=100, return_fig=None, ax=None, show=None, save=None)¶
Barplot visualization for effects.
The effect results for each covariate are shown as a group of barplots, with intra–group separation by cell types. The covariates groups can either be ordered along the x-axis of a single plot (plot_facets=False) or as plot facets (plot_facets=True).
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.covariates (
str|list|None) – The name of the covariates in data.obs to plot. Defaults to None.parameter (
Literal['log2-fold change','Final Parameter','Expected Sample']) – The parameter in effect summary to plot. Defaults to “log2-fold change”.plot_facets (
bool) – If False, plot cell types on the x-axis. If True, plot as facets. Defaults to True.plot_zero_covariate (
bool) – If True, plot covariate that have all zero effects. If False, do not plot. Defaults to True.plot_zero_cell_type (
bool) – If True, plot cell type that have zero effect. If False, do not plot. Defaults to False.figsize (
tuple[float,float] |None) – Figure size. Defaults to None.palette (
str|ListedColormap|None) – The seaborn color map for the barplot. Defaults to cm.tab20.level_order (
list[str]) – Custom ordering of bars on the x-axis. Defaults to None.args_barplot (
dict|None) – Arguments passed to sns.barplot. Defaults to None.
- Return type:
- Returns:
Depending on plot_facets, returns a
Axes(plot_facets = False) orFacetGrid(plot_facets = True) object
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> sccoda.plot_effects_barplot(mdata)
- Preview:
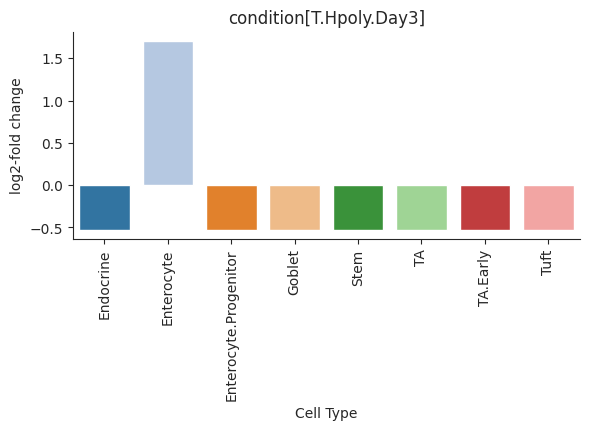
plot_effects_umap¶
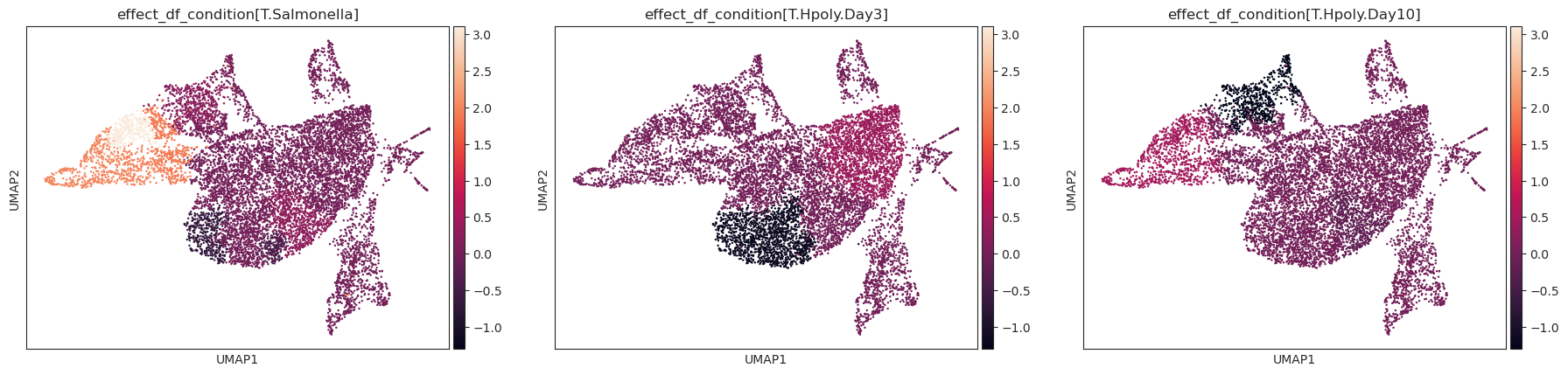
- Sccoda.plot_effects_umap(mdata, effect_name, cluster_key, modality_key_1='rna', modality_key_2='coda', color_map=None, palette=None, return_fig=None, ax=None, show=None, save=None, **kwargs)¶
Plot a UMAP visualization colored by effect strength.
Effect results in .varm of aggregated sample-level AnnData (default is data[‘coda’]) are assigned to cell-level AnnData (default is data[‘rna’]) depending on the cluster they were assigned to.
- Parameters:
mudata – MuData object.
effect_name (
str|list|None) – The name of the effect results in .varm of aggregated sample-level AnnData to plotcluster_key (
str) – The cluster information in .obs of cell-level AnnData (default is data[‘rna’]). To assign cell types’ effects to original cells.modality_key_1 (
str) – Key to the cell-level AnnData in the MuData object. Defaults to “rna”.modality_key_2 (
str) – Key to the aggregated sample-level AnnData object in the MuData object. Defaults to “coda”.show (
bool) – Whether to display the figure or return axis. Defaults to None.ax (
Axes) – A matplotlib axes object. Only works if plotting a single component. Defaults to None.**kwargs – All other keyword arguments are passed to scanpy.plot.umap()
- Return type:
- Returns:
If show==False a
Axesor a list of it.
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> import scanpy as sc >>> import schist >>> adata = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sc.pp.neighbors(adata) >>> schist.inference.nested_model(adata, n_init=100, random_seed=5678) >>> tasccoda_model = pt.tl.Tasccoda() >>> tasccoda_data = tasccoda_model.load(adata, type="cell_level", >>> cell_type_identifier="nsbm_level_1", >>> sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"], >>> levels_orig=["nsbm_level_4", "nsbm_level_3", "nsbm_level_2", "nsbm_level_1"], >>> add_level_name=True) >>> tasccoda_model.prepare( >>> tasccoda_data, >>> modality_key="coda", >>> reference_cell_type="18", >>> formula="condition", >>> pen_args={"phi": 0, "lambda_1": 3.5}, >>> tree_key="tree" >>> ) >>> tasccoda_model.run_nuts( ... tasccoda_data, modality_key="coda", rng_key=1234, num_samples=10000, num_warmup=1000 ... ) >>> tasccoda_model.run_nuts( ... tasccoda_data, modality_key="coda", rng_key=1234, num_samples=10000, num_warmup=1000 ... ) >>> sc.tl.umap(tasccoda_data["rna"]) >>> tasccoda_model.plot_effects_umap(tasccoda_data, >>> effect_name=["effect_df_condition[T.Salmonella]", >>> "effect_df_condition[T.Hpoly.Day3]", >>> "effect_df_condition[T.Hpoly.Day10]"], >>> cluster_key="nsbm_level_1", >>> )
- Preview:
plot_rel_abundance_dispersion_plot¶
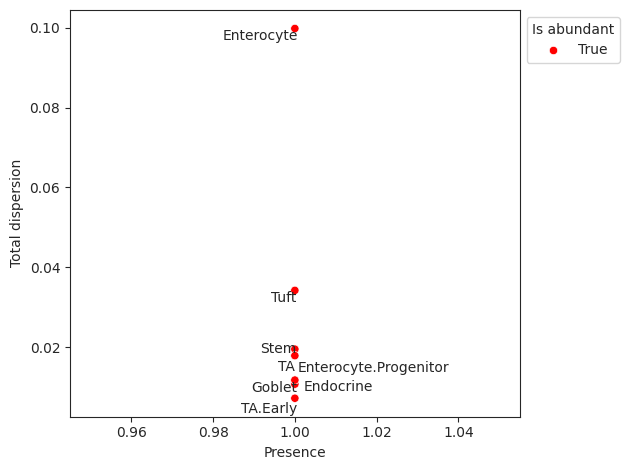
- Sccoda.plot_rel_abundance_dispersion_plot(data, modality_key='coda', abundant_threshold=0.9, default_color='Grey', abundant_color='Red', label_cell_types=True, figsize=None, dpi=100, return_fig=None, ax=None, show=None, save=None)¶
Plots total variance of relative abundance versus minimum relative abundance of all cell types for determination of a reference cell type.
If the count of the cell type is larger than 0 in more than abundant_threshold percent of all samples, the cell type will be marked in a different color.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData or MuData object.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”. Defaults to “coda”.abundant_threshold (
float|None) – Presence threshold for abundant cell types. Defaults to 0.9.default_color (
str|None) – Bar color for all non-minimal cell types. Defaults to “Grey”.abundant_color (
str|None) – Bar color for cell types with abundant percentage larger than abundant_threshold. Defaults to “Red”.label_cell_types (
bool) – Label dots with cell type names. Defaults to True.figsize (
tuple[float,float] |None) – Figure size. Defaults to None.ax (
Axes|None) – A matplotlib axes object. Only works if plotting a single component. Defaults to None.
- Return type:
- Returns:
A
Axesobject
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> sccoda.plot_rel_abundance_dispersion_plot(mdata)
- Preview:
plot_stacked_barplot¶
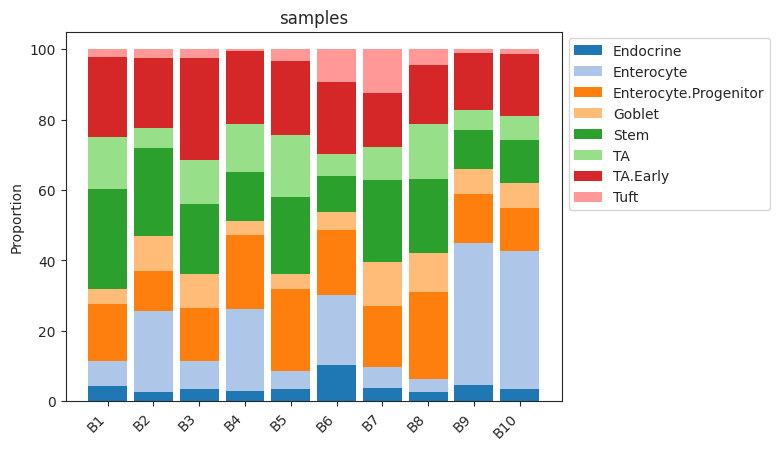
- Sccoda.plot_stacked_barplot(data, feature_name, modality_key='coda', palette=<matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap object>, show_legend=True, level_order=None, figsize=None, dpi=100, return_fig=None, ax=None, show=None, save=None, **kwargs)¶
Plots a stacked barplot for all levels of a covariate or all samples (if feature_name==”samples”).
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.feature_name (
str) – The name of the covariate to plot. If feature_name==”samples”, one bar for every sample will be plottedmodality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.figsize (
tuple[float,float] |None) – Figure size. Defaults to None.palette (
ListedColormap|None) – The matplotlib color map for the barplot. Defaults to cm.tab20.show_legend (
bool|None) – If True, adds a legend. Defaults to True.level_order (
list[str]) – Custom ordering of bars on the x-axis. Defaults to None.
- Return type:
- Returns:
A
Axesobject
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> sccoda.plot_stacked_barplot(mdata, feature_name="samples")
- Preview:
prepare¶
- Sccoda.prepare(data, formula, reference_cell_type='automatic', automatic_reference_absence_threshold=0.05, modality_key='coda')[source]¶
Handles data preprocessing, covariate matrix creation, reference selection, and zero count replacement for scCODA.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – Anndata object with cell counts as sample_adata.X and covariates saved in sample_adata.obs.formula (
str) – R-style formula for building the covariate matrix. Categorical covariates are handled automatically, with the covariate value of the first sample being used as the reference category. To set a different level as the base category for a categorical covariate, use “C(<CovariateName>, Treatment(‘<ReferenceLevelName>’))”reference_cell_type (
str) – Column name that sets the reference cell type. Reference the name of a column. If “automatic”, the cell type with the lowest dispersion in relative abundance that is present in at least 90% of samlpes will be chosen. Defaults to “automatic”.automatic_reference_absence_threshold (
float) – If using reference_cell_type = “automatic”, determine the maximum fraction of zero entries for a cell type to be considered as a possible reference cell type. Defaults to 0.05.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify key to the aggregated sample-level AnnData object in the MuData object. Defaults to “coda”.
- Return type:
AnnData|MuData- Returns:
Return an AnnData (if input data is an AnnData object) or return a MuData (if input data is a MuData object)
Specifically, parameters have been set:
adata.uns[“param_names”] or data[modality_key].uns[“param_names”]: List with the names of all tracked latent model parameters (through npy.sample or npy.deterministic)
adata.uns[“scCODA_params”][“model_type”] or data[modality_key].uns[“scCODA_params”][“model_type”]: String indicating the model type (“classic”)
adata.uns[“scCODA_params”][“select_type”] or data[modality_key].uns[“scCODA_params”][“select_type”]: String indicating the type of spike_and_slab selection (“spikeslab”)
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine")
run_hmc¶
- Sccoda.run_hmc(data, modality_key='coda', num_samples=20000, num_warmup=5000, rng_key=None, copy=False, *args, **kwargs)¶
Run standard Hamiltonian Monte Carlo sampling (Neal, 2011) to infer optimal model parameters.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.num_samples (
int) – Number of sampled values after burn-in. Defaults to 20000.num_warmup (
int) – Number of burn-in (warmup) samples. Defaults to 5000.rng_key – The rng state used. If None, a random state will be selected. Defaults to None.
copy (
bool) – Return a copy instead of writing to adata. Defaults to False.
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_hmc(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000)
run_nuts¶
- Sccoda.run_nuts(data, modality_key='coda', num_samples=10000, num_warmup=1000, rng_key=0, copy=False, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Run No-U-turn sampling (Hoffman and Gelman, 2014), an efficient version of Hamiltonian Monte Carlo sampling to infer optimal model parameters.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.num_samples (
int) – Number of sampled values after burn-in. Defaults to 10000.num_warmup (
int) – Number of burn-in (warmup) samples. Defaults to 1000.rng_key (
int) – The rng state used. Defaults to 0.copy (
bool) – Return a copy instead of writing to adata. Defaults to False.
- Returns:
Calls self.__run_mcmc
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42)
set_fdr¶
- Sccoda.set_fdr(data, est_fdr, modality_key='coda', *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
- Direct posterior probability approach to calculate credible effects while keeping the expected FDR at a certain level
Note: Does not work for spike-and-slab LASSO selection method
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Adjusts intercept_df and effect_df
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> sccoda.set_fdr(mdata, est_fdr=0.4)
set_init_mcmc_states¶
- Sccoda.set_init_mcmc_states(rng_key, ref_index, sample_adata)[source]¶
Sets initial MCMC state values for scCODA model
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Return AnnData object.
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> adata = sccoda.set_init_mcmc_states(rng_key=42, ref_index=0, sample_adata=mdata["coda"])
summary¶
- Sccoda.summary(data, extended=False, modality_key='coda', *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Printing method for the summary.
- Parameters:
data (
AnnData|MuData) – AnnData object or MuData object.extended (
bool) – If True, return the extended summary with additional statistics. Defaults to False.modality_key (
str) – If data is a MuData object, specify which modality to use. Defaults to “coda”.args – Passed to az.summary
kwargs – Passed to az.summary
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> sccoda.summary(mdata)
Examples
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, >>> type="cell_level", >>> generate_sample_level=True, >>> cell_type_identifier="cell_label", >>> sample_identifier="batch", >>> covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> sccoda.summary(mdata)
summary_prepare¶
- Sccoda.summary_prepare(sample_adata, est_fdr=0.05, *args, **kwargs)¶
- Generates summary dataframes for intercepts, effects and node-level effect (if using tree aggregation).
This function builds on and supports all functionalities from
az.summary.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Intercept, effect and node-level DataFrames
- intercept_df
Summary of intercept parameters. Contains one row per cell type.
Final Parameter: Final intercept model parameter
HDI X%: Upper and lower boundaries of confidence interval (width specified via hdi_prob=)
SD: Standard deviation of MCMC samples
Expected sample: Expected cell counts for a sample with no present covariates. See the tutorial for more explanation
- effect_df
Summary of effect (slope) parameters. Contains one row per covariate/cell type combination.
Final Parameter: Final effect model parameter. If this parameter is 0, the effect is not significant, else it is.
HDI X%: Upper and lower boundaries of confidence interval (width specified via hdi_prob=)
SD: Standard deviation of MCMC samples
Expected sample: Expected cell counts for a sample with only the current covariate set to 1. See the tutorial for more explanation
log2-fold change: Log2-fold change between expected cell counts with no covariates and with only the current covariate
Inclusion probability: Share of MCMC samples, for which this effect was not set to 0 by the spike-and-slab prior.
- node_df
Summary of effect (slope) parameters on the tree nodes (features or groups of features). Contains one row per covariate/cell type combination.
Final Parameter: Final effect model parameter. If this parameter is 0, the effect is not significant, else it is.
Median: Median of parameter over MCMC chain
HDI X%: Upper and lower boundaries of confidence interval (width specified via hdi_prob=)
SD: Standard deviation of MCMC samples
Delta: Decision boundary value - threshold of practical significance
Is credible: Boolean indicator whether effect is credible
- Return type:
Tuple[pd.DataFrame, pd.DataFrame] or Tuple[pd.DataFrame, pd.DataFrame, pd.DataFrame]
- Examples:
>>> import pertpy as pt >>> haber_cells = pt.dt.haber_2017_regions() >>> sccoda = pt.tl.Sccoda() >>> mdata = sccoda.load(haber_cells, type="cell_level", generate_sample_level=True, cell_type_identifier="cell_label", sample_identifier="batch", covariate_obs=["condition"]) >>> mdata = sccoda.prepare(mdata, formula="condition", reference_cell_type="Endocrine") >>> sccoda.run_nuts(mdata, num_warmup=100, num_samples=1000, rng_key=42) >>> intercept_df, effect_df = sccoda.summary_prepare(mdata["coda"])